Joint problems like ligament tears, cartilage damage, and shoulder injuries often limit mobility and cause persistent pain. Traditionally, open surgeries were performed to repair these issues, which required long recovery periods. However, with medical advancements, arthroscopic (keyhole) surgery has emerged as a minimally invasive alternative that allows quicker recovery, less scarring, and faster return to activity.
In this guide, we’ll explore what arthroscopic surgery is, how it is performed, the common conditions it treats, and why it has become the preferred choice for athletes and active individuals. If you’re searching for an orthopaedic surgeon in Gurugram who specializes in arthroscopy, Dr. Gaurav Arora offers advanced expertise and patient-focused care.
What is Arthroscopic Surgery?
Arthroscopic surgery, commonly known as keyhole surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat problems inside joints. A small incision is made, and a thin instrument called an arthroscope (equipped with a camera and light) is inserted into the joint. The surgeon views the joint on a monitor and performs the necessary repairs using specialized instruments.
Benefits of arthroscopy over traditional surgery:
-
Smaller incisions and minimal scarring.
-
Reduced post-surgical pain.
-
Faster recovery and rehabilitation.
-
Lower risk of infection and complications.
-
Early return to daily activities and sports.
When is Arthroscopic Surgery Recommended?
Not all joint problems require surgery, but when conservative methods fail, arthroscopy is often suggested.
Conditions commonly treated with arthroscopy include:
-
ACL / PCL Reconstruction: Restoring stability in knees after ligament tears.
-
Meniscus Repair: Repairing or removing damaged cartilage in the knee.
-
Shoulder Labral Repair: Treating shoulder instability and labral tears.
-
Rotator Cuff Repair: Reattaching torn tendons in the shoulder.
-
Ankle Arthroscopy: Treating ligament injuries, loose bodies, or cartilage damage in the ankle.
-
Cartilage Restoration: Smoothing or repairing cartilage damage in weight-bearing joints.
How Arthroscopic Surgery is Performed
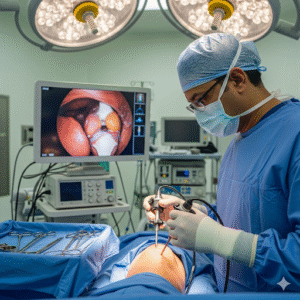
The procedure is performed under anesthesia and typically lasts between 30–90 minutes, depending on the complexity.
Step-by-step process:
-
Small incisions are made near the joint.
-
The arthroscope is inserted, projecting real-time images onto a screen.
-
Surgical tools are inserted through additional incisions.
-
Damaged tissue is repaired, removed, or reconstructed.
-
Incisions are closed with minimal sutures, and dressings are applied.
Recovery After Arthroscopy
Recovery is faster compared to traditional open surgery, but it depends on the injury and the type of repair done.
-
Immediate Post-Surgery: Patients are usually discharged the same day or within 24 hours.
-
First Few Weeks: Pain and swelling managed with ice, medication, and rest.
-
Physiotherapy: Starts soon after surgery to restore strength and mobility.
-
Return to Activities: Walking within days, light exercise in weeks, and sports in 3–6 months depending on the surgery.
Advantages of Arthroscopic Surgery for Athletes
For athletes and fitness enthusiasts, downtime is critical. Arthroscopy offers clear advantages:
-
Minimal interruption to training.
-
Lower risk of long-term stiffness.
-
Enhanced precision in repairing small but crucial structures.
-
Better long-term joint function compared to open surgery.
Risks and Limitations
While arthroscopy is considered safe, potential risks include:
-
Infection at the incision site.
-
Stiffness or swelling in the joint.
-
Rare nerve or tissue damage.
-
Longer recovery in complex cases.
It’s important to follow post-surgical advice and complete rehabilitation to minimize risks.
Arthroscopic Surgery vs Open Surgery: A Comparison
| Aspect | Arthroscopic Surgery | Open Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Incision Size | Small (keyhole incisions) | Large incision |
| Scarring | Minimal | Noticeable |
| Pain & Recovery | Less pain, faster recovery | More pain, longer recovery |
| Infection Risk | Lower | Higher |
| Hospital Stay | Day-care or short stay | Several days |
| Return to Activity | 3–6 weeks for mild cases, 3–6 months for major cases | Often 6–12 months |
Rehabilitation After Arthroscopy
Rehabilitation is as important as the surgery itself. A structured plan ensures proper healing and prevents re-injury.
Rehabilitation usually involves:
-
Phase 1 (First 2 weeks): Pain management, gentle mobility exercises.
-
Phase 2 (Weeks 2–6): Gradual strengthening of muscles around the joint.
-
Phase 3 (Weeks 6–12): Balance training, functional exercises, return to daily activities.
-
Phase 4 (Months 3–6): Sports-specific training for athletes.
Latest Advances in Arthroscopy
Modern technology has enhanced the precision and success of arthroscopic surgery.
-
3D Arthroscopy: Provides better visualization of the joint.
-
Biological Enhancements: PRP and stem cell therapy during arthroscopy to promote healing.
-
High-Definition Imaging: Improves surgical accuracy and outcomes.
Why Choose Dr. Gaurav Arora for Arthroscopic Surgery in Gurgaon?
Dr. Gaurav Arora, a leading orthopaedic surgeon in Gurugram, has extensive experience in arthroscopic procedures. His expertise covers ACL reconstruction, meniscus repair, rotator cuff repair, and advanced sports injury management. By combining minimally invasive techniques with personalized rehabilitation programs, he ensures patients regain mobility quickly and safely.
For those searching for the best orthopaedic doctor in Gurgaon for arthroscopy, Dr. Arora offers world-class care with proven results.
Arthroscopic (keyhole) surgery is revolutionizing joint treatment, offering less pain, faster recovery, and excellent long-term outcomes. Whether it’s knee, shoulder, or ankle injuries, this procedure has become the gold standard for active individuals.
If you are experiencing joint pain, ligament tears, or shoulder instability, consult Dr. Gaurav Arora, the best orthopaedic surgeon in Gurgaon, and explore advanced arthroscopic solutions for a pain-free and active life.

